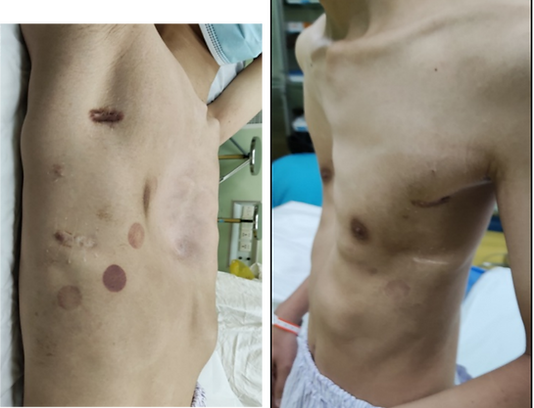
Pectus excavatum is one of the most common chest wall deformities, characterized by an inward depression of the sternum and surrounding ribs. In mild cases, it may present primarily as a cosmetic concern, but in more severe cases, the depression can compress the heart and lungs, ultimately affecting their function.
Causes and Development of the Condition
The exact cause of pectus excavatum remains unclear, but genetic factors are believed to play a significant role. During early fetal development, abnormalities in the growth of the diaphragm or costal cartilage may occur. Delayed development of the diaphragm behind the sternum, or excessively rapid growth of the costal cartilage beneath it, can create a pulling force on the sternum, gradually leading to an inward depression. Furthermore, the concave deformity worsens in most patients during puberty, even in those whose deformity was not significant during childhood.
Recognizing Pectus Excavatum Symptoms
Mild deformities usually do not interfere with daily life. In more severe cases, pectus excavatum symptoms result from compression of the heart and lungs and may include shortness of breath, palpitations, reduced stamina, frequent respiratory infections, indigestion, and chest discomfort. Psychological effects, such as anxiety or self-consciousness about appearance, are also common among teenagers and young adults. If left untreated, pectus excavatum symptoms can contribute to complications, such as scoliosis or restricted lung expansion.
Medical Assessment and Treatment Innovations
According to The Institute of Chest Wall Surgery (ICWS), evaluating the seriousness of pectus excavatum involves imaging and cardiopulmonary testing to determine whether functional impairment exists. Surgical correction is recommended for patients with severe deformities or those seeking improvement in chest appearance. ICWS’s advanced procedures, including the innovative Wang procedure, focus on safety, minimal invasiveness, and faster recovery, helping patients regain both physical health and confidence.